Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent


Study on the Damage Mechanisms and Performance Impact of Titanium Dioxide in Glass Fiber Reinforced Systems
√ When glass fiber reinforced materials need to be white
√ When your customer adds white masterbatch to the reinforced material
√ When the impact resistance of the reinforced material suddenly drops
√ When the bending strength of the material decreases
★ You should realize there's an issue between titanium dioxide (TiO₂) and glass fibers.
1. Research Background
Titanium dioxide (TiO₂), as a core component of color masterbatches, is widely used for coloring polymer materials. However, in glass fiber (GF)-reinforced composite systems, its interfacial interaction with glass fibers may induce structural damage. This study systematically quantifies the impact of TiO₂ on glass fibers and the key mechanical properties of composites through experiments.
Long glass fibers

Short glass fibers

Glass fiber powder

2. Key Findings
2.1 Structural Damage to Glass Fibers
Experimental evidence confirms that TiO₂ particles mechanically abrade glass fibers during processing, leading to microcracks on the fiber surface and, in severe cases, fiber breakage. The extent of damage is positively correlated with TiO₂ particle size, loading amount, and dispersion uniformity.
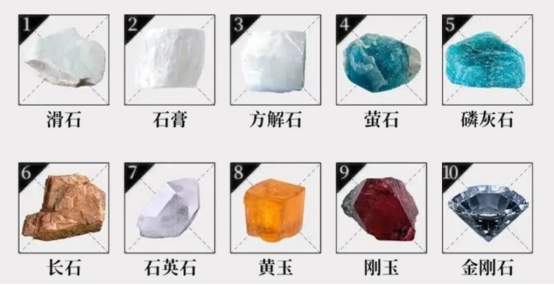
Mohs Hardness Scale Comparison
-
Glass fiber hardness: ~6.5
-
TiO₂ hardness: 6-7
√ During pelletizing, the twin-screw extruder acts like a blade, cutting glass fibers to 1mm—resulting in plastic pellets.
√ During injection molding, the screw acts like a blade, further reducing glass fibers to 0.4-0.6mm—resulting in plastic products.
√ When TiO₂ acts like a blade, it shatters glass fibers into fragments, causing a rapid decline in impact strength.
2.2 Impact Performance Degradation Mechanisms
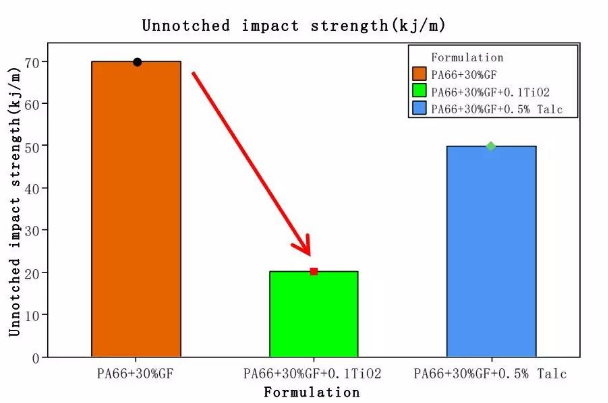
Unnotched Impact Strength:
TiO₂ reduces impact strength by ≥25%. Primary causes:
▶ Glass fiber breakage weakens the load-bearing framework.
▶ Stress concentration at TiO₂/GF interfaces.
▶ Rapid crack propagation along damaged fibers.
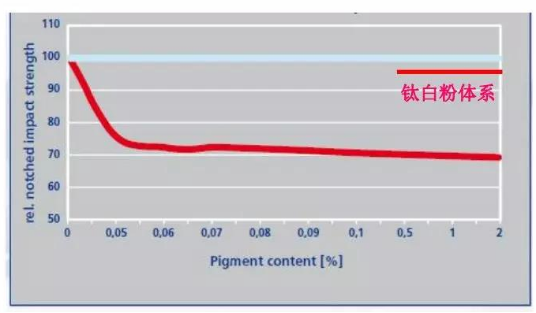
Notched Impact Strength:
Although notch behavior dominates failure, TiO₂ still reduces strength by 8-15%, reflecting its weakening effect on material toughness reserves.
2.3 Risks of Using TiO₂ Masterbatches
90% of commercial masterbatches contain TiO₂ (5-40% loading). Direct use in GF-reinforced systems irreversibly damages fiber integrity, leading to degraded impact performance in final products.
3. Conclusions & Recommendations
3.1 TiO₂ is a potential damage source in GF-reinforced systems and should be carefully evaluated:
▶ Avoid TiO₂ in non-essential coloring scenarios.
▶ If necessary, consider Longzheng's specialized white material solution:
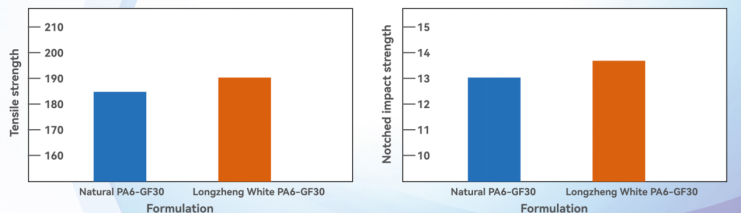
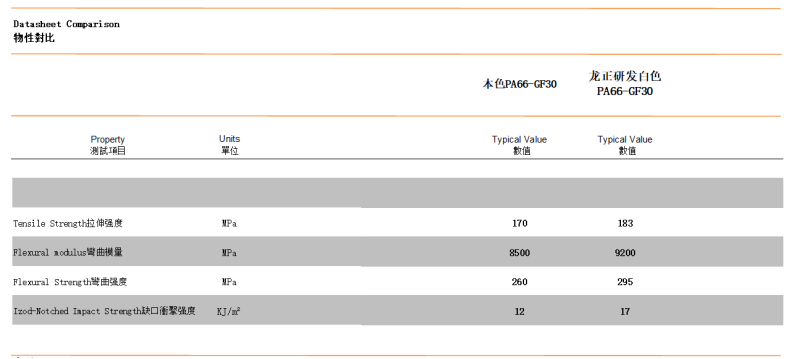
▶ Longzheng's specially developed white pigment not only prevents the decline in impact and tensile strength but, as experimental results show, even enhances these properties compared to the original uncolored material.